Retirement Plan Services
IRS Limits on Retirement Benefits and Compensation
November 5, 2024

Highlights of changes for 2025
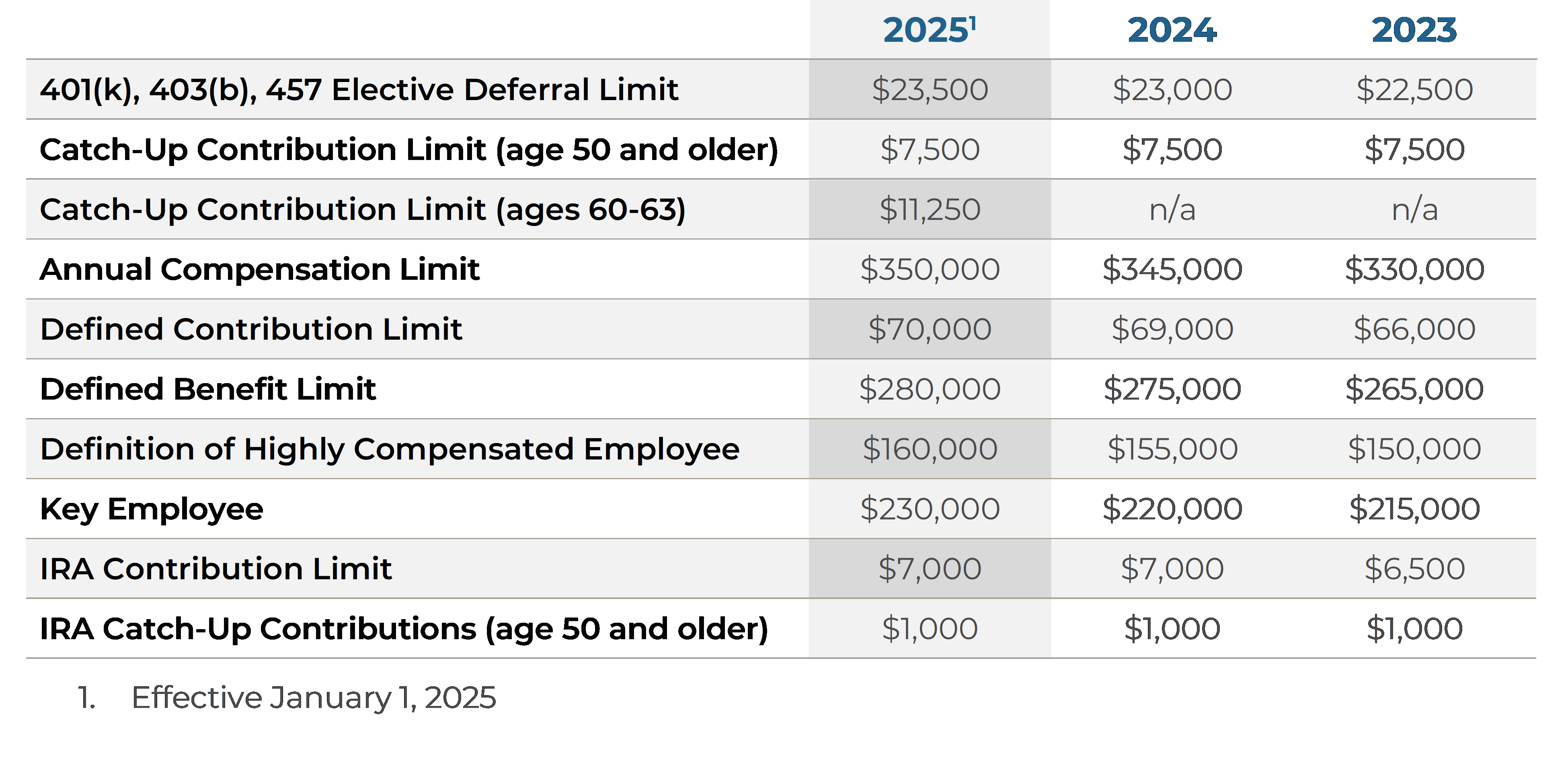
The contribution limit for employees who participate in 401(k), 403(b), most 457 plans, and the federal government’s Thrift Savings Plan increased to $23,500, up from $23,000.
The amount individuals can contribute to their SIMPLE retirement accounts increased to $16,500,
up from $16,000.
The income ranges for determining eligibility to make deductible contributions to traditional Individual Retirement Arrangements (IRAs), to contribute to Roth IRAs and to claim the Saver’s Credit all increased for 2025.
The qualified charitable distribution amount individuals can exclude from their gross income increased to $108,000 in 2024, up from $105,000 in 2024.
Taxpayers can deduct contributions to a traditional IRA if they meet certain conditions. If during the year either the taxpayer or the taxpayer’s spouse was covered by a retirement plan at work, the deduction may be reduced, or phased out, until it is eliminated, depending on filing status and income. (If neither the taxpayer nor the spouse is covered by a retirement plan at work, the phase-outs of the deduction do not apply.)
Here are the phase-out ranges for 2025:
- For single taxpayers covered by a workplace retirement plan, the phase-out range is increased to between $79,000 and $89,000, up from between $77,000 and $87,000.
- For married couples filing jointly, if the spouse making the IRA contribution is covered by a workplace retirement plan, the phase-out range is increased to between $126,000 and $146,000, up from between $123,000 and $143,000.
- For an IRA contributor who is not covered by a workplace retirement plan and is married to someone who is covered, the phase-out range is increased to between $236,000 and $246,000, up from between $230,000 and $240,000.
- For a married individual filing a separate return who is covered by a workplace retirement plan, the phase-out range is not subject to an annual cost-of-living adjustment and remains between $0 and $10,000.
- The income phase-out range for taxpayers making contributions to a Roth IRA is increased to between $150,000 and $165,000 for singles and heads of household, up from between $146,000 and $161,000. For married couples filing jointly, the income phase-out range is increased to between $236,000 and $246,000, up from between $230,000 and $240,000. The phase-out range for a married individual filing a separate return who makes contributions to a Roth IRA is not subject to an annual cost-of-living adjustment and remains between $0 and $10,000.
- The income limit for the Saver’s Credit (also known as the Retirement Savings Contributions Credit) for low- and moderate-income workers is $79,000 for married couples filing jointly, up from $76,500; $59,250 for heads of household, up from $57,375; and $39,500 for singles and married individuals filing separately, up from $38,250.
Key limits remain unchanged
The limit on annual contributions to an IRA remains $7,000. The IRA catch-up contribution limit for individuals aged 50 and over is not subject to an annual cost-of-living adjustment and remains $1,000.
The catch-up contribution limit for employees aged 50 and over who participate in these plans remains $8,500.
As published in IRS News Release IR-2024-285, November 1, 2024. Details on these and other retirement-related cost-of-living adjustments please contact your financial professional or visit irs.gov.
